DBSetup.exe - Database maintenance
Caution
From SuperOffice 11.6, ServerSetup.exe and DBSetup.exe have been discontinued and replaced by the CRMSetup.exe and CRMTask.exe command-line utilities.
Earlier versions of DBSetup may differ a bit in the user interface, but the basic functionality is still the same. Please note the warning - there is no turning back once you have started the different operations.
See also the SoTables.ini info - but with CDD note that the priming data provided by SuperOffice are no longer packaged as individual files; this function is only intended for adding new data specific to a customer or partner feature.
Since SuperOffice 8.1 DBSetup can create a Database.log file.
DbSetup/ServerSetup will create all tables, both SuperOffice and Service. DbSetup export & import supports all tables and data.
Note
DBSetup is not a backup solution. Onsite installations must use a standard database backup strategy.
The Service application installer tweaks some service related tables.
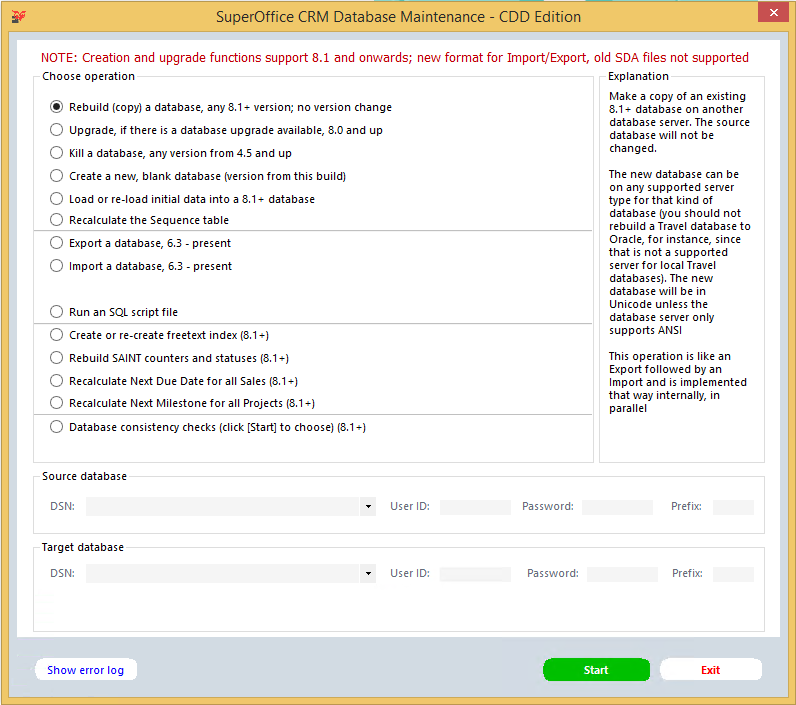
Rebuild (copy) a database, any 8.1+ version, no version change
Make a copy of an existing 8.1+ database on another database server. The source database will not be changed.
The new database can be on any supported server type for that kind of database (you should not rebuild a Travel database to Oracle, for instance since that is not a supported server for local Travel databases). The new database will be in Unicode unless the database server only supports ANSI.
This operation is like an Export followed by an Import and is implemented that way internally, in parallel.
If you use Service, please see below.
Upgrade, if there is a database upgrade available, 8.0 and up
Upgrade a database from 8.0 or later with new any changes up to this build, by updating the database schema in-place. You MUST HAVE a backup, there is no undo and no recovery in case of crash halfway.
Any version from 8.0 and up is supported.
Please note that upgrades may only be done to versions known by the SuperOffice license system (SuperLicense), but there are no limitations on how many times you may upgrade the same serial number (for testing).
Include "In development" steps - this will import also dictionary steps marked as "In Development".
Kill a database, any version from 4.5 and up
Kill a database according to its DatabaseModel-specified content, from version 4.5 and up. Data and dictionary tables are removed, including partner-defined tables and Service extra tables. Database users (obsolete functionality!) are not touched. If you have no backup, the database is gone for good.
Any table not specified in the database's model/dictionary will be left untouched.
Create a new, blank database (version from this build)
Create a new database; you will need an Internet connection and valid license information. Any existing database on the given data source will be deleted. The database will use Unicode string storage unless the server is capable of ANSI only.
If you are running an international enterprise, Unicode is necessary to be able to mix languages between Western Europe, Eastern Europe, and Asia.
Some preferences that ServerSetup writes during installation will not be written, for example, E-mail client and client auto-update.
Load or re-load initial data into an 8.1+ database
Import or update the basic (initial) data in an existing database. You can choose which section to import from the dropdown list, which shows sections defined in your SoTables.ini file.
Priming data that are part of the standard set provided by SuperOffice are no longer packaged as individual files; this function is only intended for adding new data specific to a customer or partner feature. The old impfiles may contain old data and importing it to an upgraded database may overwrite data that have been updated with a dictionary step during database upgrade.
If you leave the dropdown list blank it will just re-calculate the sequence next_id, see next operation.
Recalculate the Sequence table
Recalculate the Sequence table, by scanning all data tables.
If there is a lot of traffic on the database, the results MAY be wrong; so choose a quiet moment.
If importing an SDB file that was exported from a heavily used database, running this operation is a good idea as Sequence is exported first, and may not be fully up to date in the SDB file.
Export a database, 6.3 - present
Export the entire database to a flat file. Note that the SDB format in this version is not compatible with previous SDA formats. Both SuperOffice and registered partner data, as well as Customer Service extra fields/tables are exported.
Supported versions are 6.3 and later.
The file is written in a compressed format and won't compress further.
Import a database, 6.3 - present
Import a database from a flat file created by the Export function; only the current SDB format is supported, not the earlier SDA. Any existing database on the target WILL BE DELETED!
The resulting database will be in the original version, no upgrade is performed; however, platform conversion (for instance, Oracle 11g -> MSSQL 2016) is done as needed.
You should use a database user with rights to perform DROP TABLE, CREATE TABLE, and user administration commands. The new database will be in Unicode format unless the server is only capable of ANSI.
Obsolete from 8.1 - CDD: Inspect a database or export a file
Open an import file OR database and retrieve some information from it. This command will not make any changes to any database, just use it to peek inside.
If an import file name is specified, then that file will be inspected; otherwise, the Source database specification will be used and a database will be inspected.
Run a SQL script file
Load a text file and run SQL statements in it. Statements are separated/terminated by a semicolon character.
Warning
No checks are made - if you mess up the database "by accident", it's your problem...
Create or re-create free-text index (8.1+)
Create or update the free-text index on an existing 8.1+ database. The same function is available in the Admin client.
Note
To perform this task, the SuperOffice.config user needs to be a valid associate or a system user and Table Admin user set in Win Admin needs to be a valid database user.
Rebuild SAINT counters and statuses (8.1+)
Perform a total rebuild of the SAINT counters, and subsequently the SAINT status flags. Depending on the number of contacts, project, appointments, sales, and intent list entries, this can be a fairly lengthy process.
This task may also be automated by using the Travel gateway service.
Note
To perform this task, the SuperOffice.config user needs to be a valid associate or a system user and Table Admin user set in Win Admin needs to be a valid database user.
Recalculate Next Due Date for all Sales (8.1+)
Scan all appointments bound to sales, and update the Next Due Date on all sales. Depending on the number of sales and appointments, this can be a fairly lengthy process.
The user name must be a valid employee or system user, not just a database user.
Recalculate Next Milestone for all Projects (8.1+)
Scan all appointments bound to a project, and update the Next Milestone on all projects. Depending on the number of sales and appointments, this can be a fairly lengthy process.
The user name must be a valid employee or system user, not just a database user.
Database consistency checks (click[Start] to choose) (8.1+)
Run consistency checks on the target database; and fix what problems may be fixed automatically.
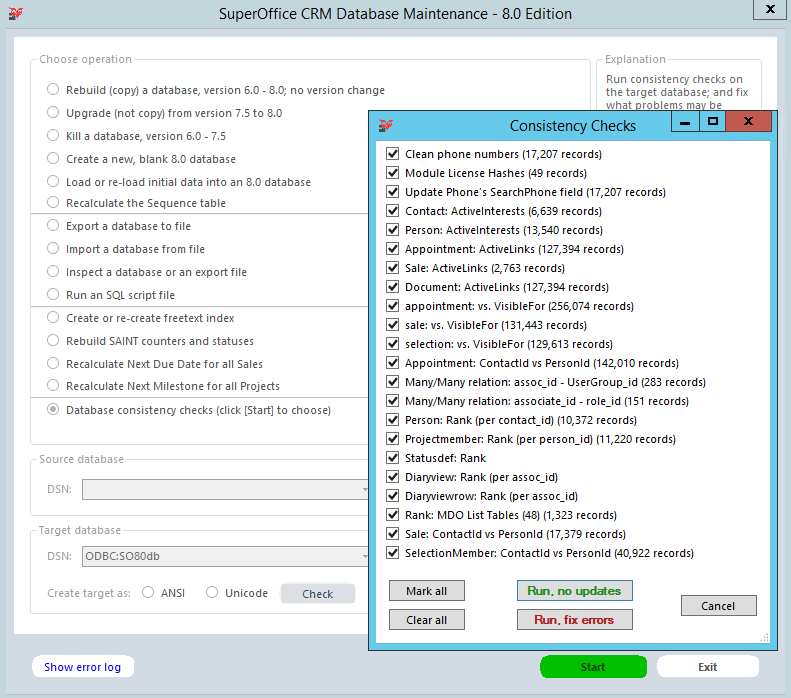
When you press Start you will be presented with a choice of checks to run, and estimates of the size of each check.
Here you may run and fix problems found in the database:
- Clean phone numbers - will remove wrong values stored in the database, like InterAreaPrefix (0), DialInCode (like +47), and so on
- Reset all external user licenses
- Module License Hashes
- Update Phone's SearchPhone field
- ActiveInterests count on Contact and Person.
- ActiveLinks on Appointment, Sale, and Document.
- VisibleFor on Appointment, Sale, Selection
- ContactId vs PersonId on Appointment - when the Contact_id on the appointment refers to a different contact than the person you will get the "jumping activity syndrome" where clicking the activity archive automatically refers you to another company card. Running this option will fix this problem.
- Many/many relation on Assoc_id - UserGroup and Associate_id - role_id
- Many/many relation on Associate_id - role_id
- Person: Update persons rank pr contact_id - import will not calculate rank correctly so this will fix it.
- Projectmember: rank (per person_id)
- StatusDef: Rank
- DiaryView: Rank (per assoc_id)
- DiaryViewRow: Rank (per assoc_id)
- Rank: MDO List Tables
- Sale: ContactId vs PersonId
- SelectionMember: ContactId vs PersonId
If you have imported data to the SuperOffice database via SOAdmin we recommend you run these to verify that the rank is set correctly. Rank will not be set during import due to performance issues.
Start DBSetup with parameters
Dbsetup.exe can be run with command line parameters to specify an action. The program will perform the action automatically and exit. User interaction may occur if something goes wrong (this may be corrected in a future version ).
The command line consists of a command followed by parameters. They correspond to the radio buttons in the GUI.
Parameters also correspond to the GUI. Parameters are separated by spaces and all are required. Note that this means that blank passwords are not supported.
| Command | Param count | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| REBUILD | 9 | Source DSN, user, password and prefix (remember ODBC: for ODBC databases), target DSN, user, password, prefix, and A for Ansi or U for Unicode |
| UPGRADE70 | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| CREATE7 | 16 | DSN, User, Password, Prefix, A for Ansi/ U for unicode target, [Contact name, Country id, First name, Last name, User ID, Password, Serialnumber] |
| IMPORTINITIAL | 5 | DSN, user, password, prefix, name of the section in SOTABLES.INI to import tables for |
| FREETEXTINDEX | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| KILLDATABASE | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| MAINTENANCE | ||
| IMPORT | 5 | DSN, user, password, prefix, name, and path to file |
| EXPORT | 5 | DSN, user, password, prefix, name, and path to file |
| REBUILDSAINT | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| NEXTMILESTONE | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| SYNCUSERS | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| RECALCSEQUENCE | 4 | DSN, user, password, and prefix |
| RUNCHECKS | 5 | DSN User, Password, Prefix, Semicolon-separated list of Check names |
| RUNSQL | 5 | DSN, user, password, prefix, name, and path to SQL query file |
Possible check names::
- Phone CleanPhone
- moduleHash
- Phone SearchPhone
- contactActiveCountactiveInterests
- personActiveCountactiveInterests
- appointmentActiveCountactiveLinks
- saleActiveCountactiveLinks
- documentActiveCountactiveLinks
- appointmentVisibleFor
- saleVisibleFor
- selectionVisibleFor
- appointmentContactPersonId
- linkassoc_idUserGroup_id
- linkassociate_idrole_id
- personRank
- projectmemberRank
- statusdefRank
- diaryviewRank
- diaryviewrowRank
- mdoRanks
- saleContactPersonId
- selectionContactPersonId
An error message is given if the supplied command line has the wrong command or number of parameters. Normal errors are given for other problems, such as the wrong password. If everything is OK, normal progress dialogs are shown, but the program terminates automatically after execution.
DBSetup Database log file
Since SuperOffice 8.1 is DBSetup able to create a Database.log file, which contains detailed and valuable database debugging information. To get this file you need to have the [Error] section in SuperOffice.ini in the SuperOffice Server folder (where DBsetup.exe resides) and also specify the location of the log file (without the Logpath the Database.log file won't be created).
Example of the [Error] section in SuperOffice.ini in SuperOffice Server folder:
[Error]
EnableOleDbLog=0
EnableReporterLog=0
EnableDebug=0
Truncate=1
Logpath=e:\SuperOffice\SOError.log
If you run DBSetup now, it will create 2 log files in E:\SuperOffice. One standard SOError.log file and one SOError.Database.log file with database debug information.
The Database.log file is also generated by ServerSetup when a database upgrade happens and goes into the same place that so_log.txt does unless specified otherwise by the LogPath in the [Error] section.
Note
If you are using DBSetup to rebuild or move a database, you MUST run <service installfolder>\bin\Upgrade.exe after to set the Service fields values correct.
NULL Values (may be used on some fields made in Service): DBsetup does not have the data structures/flags required to carry this additional information. So, when doing a rebuild/import of a database that contains NULL values (some Service tables do), those will be changed into the nearest-to-empty value for that type - empty string, number 0, and so on.